Introduction
DevOps is a methodology that brings together the development and operations teams to achieve faster and more reliable software delivery. This approach facilitates collaboration, communication and automation in the software development process thus increasing productivity of all stakeholders.
DevOps methodology ensures continuous delivery by relying on the principles of continuous integration, continuous testing and continuous deployment. It also emphasizes on the impotence of automation for speeding up the process, decrease errors and increase the efficiency of the process.
So, DevOps as a methodology basically promotes better collaboration so that everyone involved is working towards the same goals and any challenges can be addressed and resolved quickly. DevOps methodology helps software development companies improves their processes, reduce costs and increase customer satisfaction.
1. Importance of DevOps methodology
In this fast paced digital world, DevOps methodology is becoming highly important. Its ability to break down silos and allow cross functional collaboration leads to a streamlined software development process.
One of the key benefits of DevOps methodology is the ability to continuously deliver software updates and improvements. This means that software is updated and released more frequently, allowing organizations to respond quickly to changes in the market and to customer feedback. This can help organizations to stay ahead of the competition, as they are able to deliver new features and functionality faster and more frequently.
Another important benefit of DevOps methodology is the focus on automation. By automating repetitive tasks, such as testing and deployment, organizations can reduce the risk of errors and speed up the software development process. This not only saves time but also reduces costs and ensures that software is delivered on time and on budget. Additionally, automation allows developers to focus on more creative and strategic tasks, such as developing new features and improving user experience, which can further enhance the value of the software product.
2. Brief history of DevOps
DevOps methodology came into being in the early 2000s when there was an increasing demand of efficient and agile approaches of software development. While Agile methodology was gaining popularity in those days and emphasized an iterative and collaborative approach to software development, as well as continuous feedback and improvement. But , there was still a disconnect between development and operations teams because agile focussed on the development process.
To bridge this gap, DevOps methodology was designed in which development and operations teams could collaborate throughout the software development lifeycle to increase overall efficiency and speed of the process.
3. Key principles of DevOps
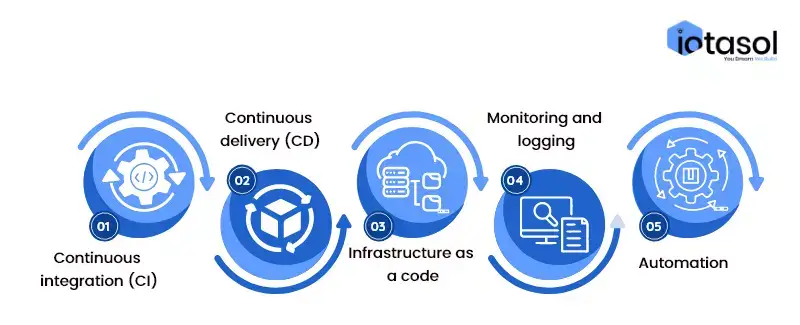
a. Continuous integration (CI)
Continuous Integration is a key principle in DevOps methodology that refers to the usage of a shared repository for integrating all the code changes from all the developers at this centralized place. It involves automatically building, testing, and validating the changes to ensure that they are compatible with the existing codebase and do not introduce any errors or conflicts.
Its major goal is to catch and bring attention to any defects or bugs at the earliest in software development lifecycle. Continuous Integration helps developers in resolving defects quickly so that their is no possibility of introducing defects in the codebase.
This way, code is always in deployable state and can be released to production ith confidence.
b. Continuous delivery (CD)
Continuous Delivery (CD) is a practice in DevOps methodology that focuses on automating the entire software delivery process, from code changes to production deployment. It involves building, testing, and releasing software changes frequently and reliably, allowing organizations to deliver new features and updates to their customers quickly and efficiently.
The primary goal of CD is to streamline the software delivery process and reduce the time and effort required to release software updates. It involves the use of automation tools and processes to automate the build, test, and deployment of software changes, ensuring that they are ready for production at any time.
CD builds upon the concept of Continuous Integration (CI), which focuses on integrating code changes frequently and validating them through automated testing. In CD, the validated code changes are automatically deployed to production, eliminating the need for manual intervention.
c. Infrastructure as a code
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is a practice in DevOps methodology that involves managing and provisioning infrastructure using code and automation tools, rather than manual processes or ad-hoc configuration changes. It treats infrastructure as a software system that can be defined, versioned, and tested just like any other code. The main goal of IaC is to enable teams to manage infrastructure in a more agile and efficient way, by using code to define the desired infrastructure state and automate the provisioning process.
d. Monitoring and logging
Monitoring and logging are two critical practices in DevOps methodology that enable teams to detect and troubleshoot issues in real-time, and ensure that applications are performing as expected.
Monitoring involves tracking and measuring the performance and health of applications, infrastructure, and services in real-time. It involves the use of tools that collect and analyze data, such as metrics, events, and logs, to provide visibility into system behavior and detect issues as soon as they occur. Monitoring can help teams identify performance bottlenecks, diagnose errors and outages, and optimize system performance.
Logging, on the other hand, involves capturing and storing information about application and system behavior, such as errors, warnings, and other relevant events. Logs can be used to track system activity, diagnose issues, and audit system behavior. They can also be used to analyze system performance and identify trends and patterns over time.
e. Automation
In DevOps technology, automation refers to the process of using software tools and technologies to automate the various stages of the software development, testing, deployment, and maintenance processes.
Automation is a critical aspect of DevOps as it enables organizations to streamline their software delivery processes, reduce errors, increase efficiency, and improve the overall quality of their software products.
Some common examples of automation in DevOps include automated testing, continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD), configuration management, infrastructure as code (IaC), and monitoring and alerting. By automating these processes, organizations can accelerate the delivery of software while reducing the risks associated with human error and manual intervention.
4. DevOps tools and technologies
a. Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD) Tools
These tools are used to automate the build, testing, and deployment of applications. Some popular CI/CD tools include Jenkins, GitLab CI/CD, CircleCI, Travis CI, and TeamCity.
b. Containerization Tools
Containerization tools enable developers to package their applications and dependencies into portable, isolated containers that can run on any infrastructure. Some popular containerization tools include Docker, Kubernetes, and Apache Mesos.
c. Monitoring and Logging Tools
These tools are used to monitor and track the performance and behavior of applications and infrastructure. Some popular monitoring and logging tools include Prometheus, Grafana, Nagios, ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana), and Splunk.
d. Collaboration and Communication Tools
These tools enable developers and operations teams to collaborate and communicate effectively. Some popular collaboration and communication tools include Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Atlassian's Jira and Confluence.
e. Cloud Computing Platforms
Cloud computing platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform provide infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS) offerings that enable organizations to deploy and scale their applications and services quickly and efficiently.
f. Version Control Tools
Version control tools such as Git and SVN are used to manage changes to code and track different versions of applications.
These are just a few examples of the many tools and technologies available for DevOps. The key is to select the tools and technologies that best fit your organization's needs and requirements and integrate them effectively to achieve your DevOps goals.
